Cancer is a devastating disease that can affect anyone regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is the second leading cause of death globally, with an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018. Early detection and cancer screening guidelines are essential in reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with cancer.
What is cancer screening?
Cancer screening involves testing for cancer in people who have no symptoms. The goal of cancer screening is to detect cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable. Early detection of cancer can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased chances of survival.
Why is early detection important?
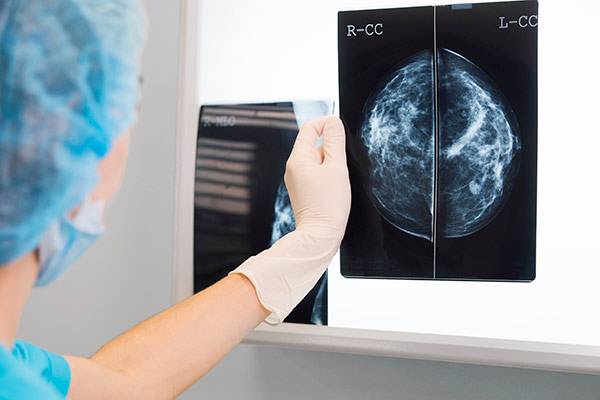
Early detection is crucial in the fight against cancer. When cancer is detected early, it is easier to treat and has a better chance of being cured. Early detection can also reduce the need for more invasive and aggressive treatments, which can have significant side effects and impact a person’s quality of life.
What are cancer screening guidelines?
Cancer screening guidelines are recommendations for when and how often people should be screened for certain types of cancer. These guidelines are based on a person’s age, gender, and risk factors for cancer. The most commonly recommended cancer screenings include mammograms for breast cancer, Pap tests for cervical cancer, and colonoscopies for colon cancer.
Who should get screened for cancer?
Screening recommendations vary depending on the type of cancer. However, in general, people who are at average risk for cancer should start getting screened at a certain age. For example, women should start getting mammograms for breast cancer at age 50, and men and women should start getting colonoscopies for colon cancer at age 45 or 50. People who are at increased risk for cancer, such as those with a family history of cancer, may need to start screening at an earlier age or get screened more frequently.
What are the benefits and risks of cancer screening?
The benefits of cancer screening include early detection, which can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased chances of survival. However, there are also risks associated with cancer screening, such as false-positive results, which can lead to unnecessary testing and procedures. There is also a risk of overdiagnosis, which occurs when cancer is detected and treated that would not have caused harm if left untreated. It is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of cancer screening with your doctor to determine if screening is right for you.
Early detection and cancer screening guidelines are essential in reducing the burden of cancer. Screening can detect cancer at an early stage when it is more treatable and can lead to better treatment outcomes and increased chances of survival. However, it is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of cancer screening with your doctor to determine if screening is right for you. By following cancer screening guidelines, we can work together to prevent and detect cancer early, ultimately saving lives.