As a resident living with arthritis can be a daunting challenge. Foot arthritis, in particular, can make everyday activities like walking, standing, and even simple tasks around the house a painful ordeal. However, managing arthritis symptoms doesn’t have to rely solely on medication or surgery. Research has shown that a well-planned diet can play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and alleviating arthritis symptoms. As a trusted Maryville, IL foot arthritis specialist, we recommend incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet into your lifestyle to help manage arthritis symptoms and improve overall health.
In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet and provide practical tips on how to make sustainable dietary changes to help you take control of your arthritis symptoms.
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Characterized by the degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone, arthritis can manifest in various forms, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout, among others. With over 100 different types, arthritis can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or ethnicity, impacting daily life and overall well-being.
What is The Link Between Diet and Arthritis?
Research has shown that diet plays a crucial role in the development and management of arthritis. Certain foods can trigger inflammation, while others can help reduce it. The key is to identify the foods that can help alleviate arthritis symptoms and incorporate them into your diet.
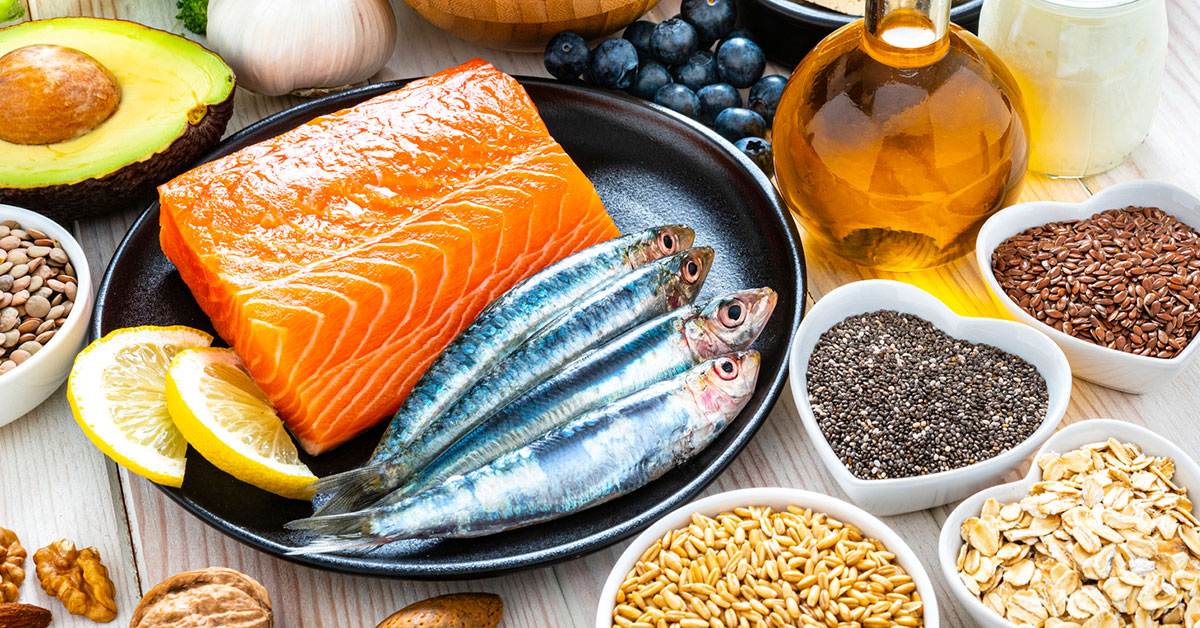

What Foods Can Reduce Inflammation?
Here are some of the top anti-inflammatory foods that can help reduce arthritis symptoms:
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and alleviate arthritis symptoms.
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains a powerful anti-inflammatory compound called curcumin. Curcumin has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve arthritis symptoms.
- Ginger: Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and inflammation. It can be consumed raw, cooked, or in supplement form.
- Leafy Greens: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in antioxidants and other anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds like walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in healthy fats and antioxidants.
What Are The Foods That Can Exacerbate Inflammation?
Here are some of the top foods that can exacerbate inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms:
- Processed Meats: Processed meats like hot dogs, sausages, and bacon contain advanced glycation end (AGE) products. AGEs can stimulate inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms.
- Refined Sugars: Refined sugars can cause inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms.
- Dairy Products: Dairy products contain a protein called casein, which can stimulate inflammation in some people.
- Gluten: Gluten can cause inflammation in people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
- Fried Foods: Fried foods are high in inflammatory compounds like omega-6 fatty acids.
What Are The Tips For Incorporating Anti-Inflammatory Foods Into Your Diet?
Here are some tips for incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into your diet:
- Start with Small Changes: Start by making small changes to your diet, such as adding a serving of fatty fish or leafy greens to your meals.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Inflammatory Foods: Avoid foods that can exacerbate inflammation, such as processed meats, refined sugars, and fried foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Consider Supplements: Consider taking supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger to support anti-inflammatory effects.
Remember to start with small changes, focus on whole foods, and stay hydrated to support anti-inflammatory effects. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized diet plan that meets your unique needs and health goals.